A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed server network designed to speed up web content delivery by placing it closer to users. CDNs use caching, temporarily storing copies of files globally, reducing page load times for an improved web experience. Caching content like web pages, images, and videos on nearby servers facilitates quick access to activities like watching movies, downloading software, and more.
Think of CDNs like ATMs; if your money were only accessible from one bank, you'd face time-consuming trips. Instead, CDNs, like scattered ATMs, provide fast access to content. Initially addressing network congestion from rich web content, CDNs now cover text, graphics, scripts, media files, software downloads, documents, portals, ecommerce, live streaming, on-demand video, and social media.
For over two decades, CDNs have silently been the internet's “backbone”, enhancing website performance and efficiently delivering online content at scale. A significant portion of internet content is now transmitted through CDNs.
How does a CDN work?
A content delivery network relies on 3 types of servers:
- Origin servers: These servers house the original versions of content and serve as the definitive source. Any necessary updates to the content are made on the origin server, which may be owned by the content provider or hosted on a third-party cloud provider's infrastructure, such as VNG Cloud.
- Edge servers: Positioned in various global locations, also known as "points of presence" (PoPs), edge servers cache content obtained from origin servers. They are responsible for delivering this cached content to nearby users. When a user requests access to content on an origin server, they are directed to a cached copy on an edge server in close geographical proximity. If the cached content is outdated, the edge server retrieves updated content from the origin server. CDN edge servers are owned or managed by the CDN hosting provider.
- DNS servers: The Domain Name System (DNS) servers keep records and provide IP addresses for both origin and edge servers. When a client submits a request to an origin server, DNS servers reply with the name of a paired edge server from which the content can be served more rapidly.
A significant share of internet content is distributed via CDNs. Here's a practical overview of how it operates:
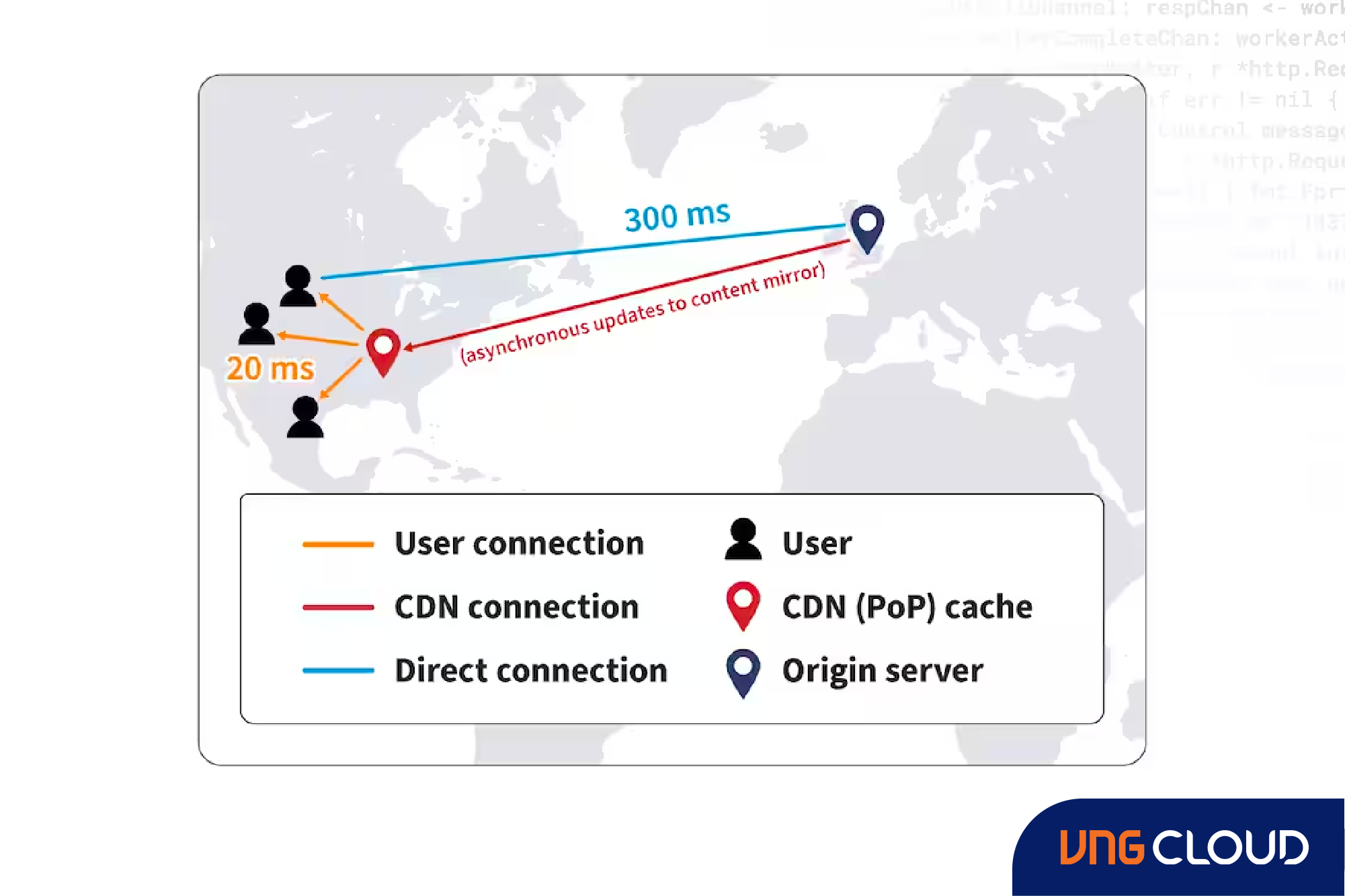
To ensure an optimal viewing experience, CDNs perform two crucial functions:
- Reduce latency: Latency, the frustrating delay encountered when accessing a web page or video stream, is addressed by CDNs. Though measured in milliseconds, this delay can feel prolonged and lead to load errors. CDNs mitigate latency by minimizing the physical distance content needs to travel to reach the user. Consequently, larger and more widely distributed CDNs enhance the speed and reliability of delivering website content by placing it as close to the end user as possible.
- Balance loads: CDNs evenly distribute overall traffic to enhance the web experience for everyone accessing internet content. Analogous to managing traffic in the real world, CDNs optimize routes. While there might be a typically faster route from point A to point B, traffic is redirected to alternative routes in the event of congestion. This may result in a slightly longer journey (or milliseconds in the context of internet speeds), but it prevents users from getting stuck in a traffic jam on the shortest route. Load balancing enables content providers to handle increased demand and significant traffic spikes, ensuring high-quality user experiences and avoiding downtime.
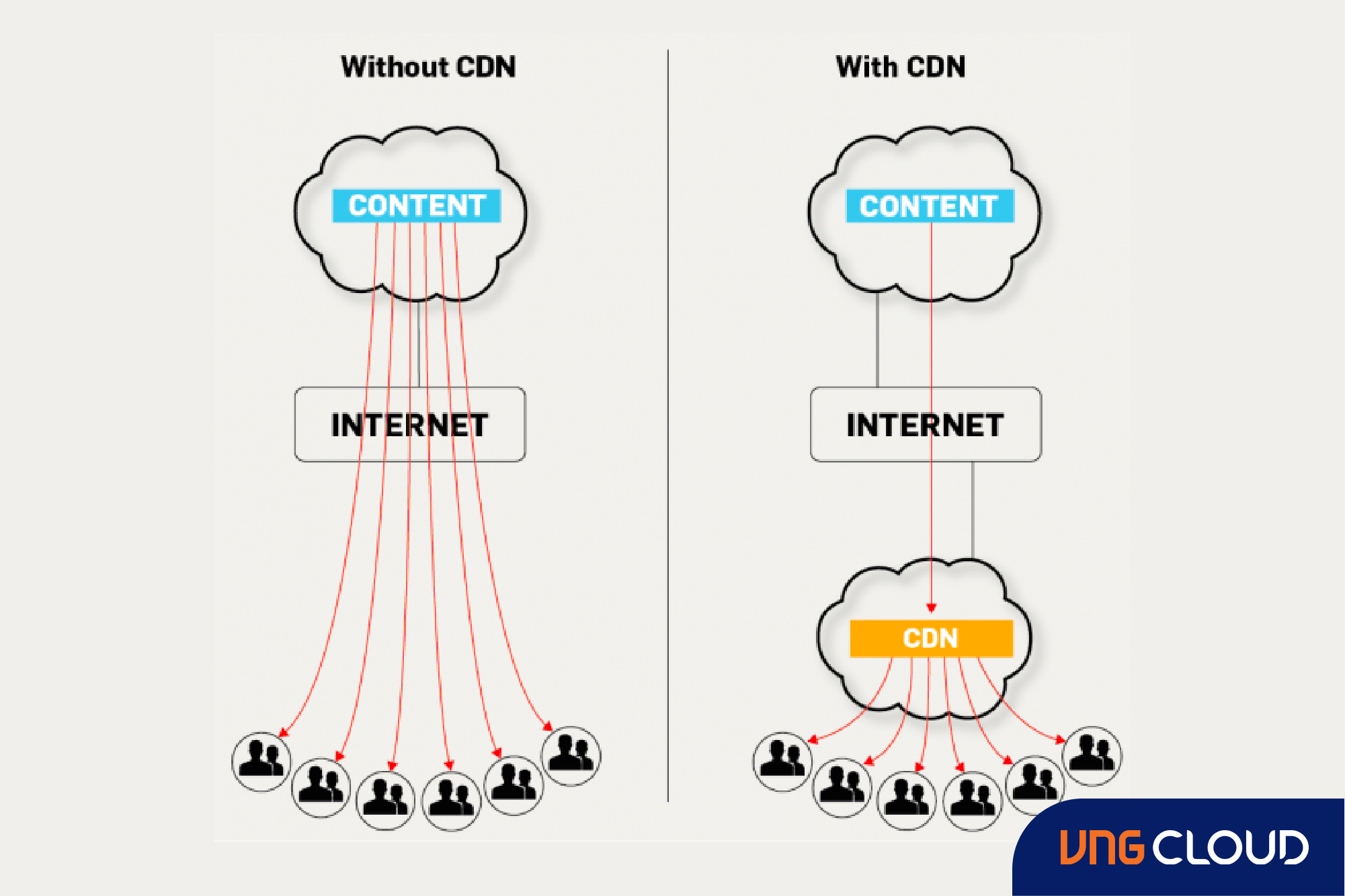
The benefits of a CDN
CDNs handle a significant share of global internet traffic, addressing the most challenging aspects of content delivery online. Businesses of all sizes, from small and medium content providers to major corporations worldwide, leverage the essential benefits of CDNs to ensure a smooth web experience for their customers.
- Optimize performance: CDNs play a pivotal role in speeding up content delivery, ensuring a seamless experience by minimizing buffering and reducing load times. They achieve this by delivering pre-saved content from nearby servers on the CDN's network, bypassing the need to send requests to distant origin servers. Advanced CDNs utilize additional technologies to address challenges in delivering uncacheable dynamic content and tailor content types to different devices, resulting in faster web page rendering and reduced video buffering times.
- Ensure availability: CDNs offer a robust solution to maintain content accessibility even during peak user traffic or server outages. With a widely distributed infrastructure capable of absorbing massive traffic loads, advanced CDNs can handle over 100 TBps of traffic, ensuring content providers stay available to larger user bases.
- Enhance security: CDNs contribute to improved website security by providing increased protection against threats such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Advanced CDNs offer unique cloud-based security solutions and DDoS protection.
- Gather intelligence: As carriers of nearly half of the world's internet traffic, CDNs generate extensive data on end-user connectivity, device types, and browsing experiences globally. This data enables CDN customers to gain actionable intelligence, supporting services like real user monitoring, media analytics, and cloud security intelligence to track online threats.
- Improve customer experiences: Various content, application, and website owners leverage CDNs to enhance customer experiences, reducing abandonment rates, increasing ad impressions, improving conversion rates, and fostering customer loyalty.
- Offload traffic: With the surge in online streaming and rich media services, CDNs help alleviate stress on network service providers by responding to content requests with cached versions from servers closer to end users, improving overall web experiences.
- Reduce bandwidth costs: CDNs lower bandwidth consumption and associated costs by delivering content from nearby servers, reducing the need for extensive data transfer across long distances.
Who uses CDNs?
Almost everyone accessing the internet relies on a CDN, which was designed to offer a quicker and more dependable online experience. Content and application owners, along with network service providers, utilize CDNs to deliver these advantages to their customers.

Education
Educational institutions leverage CDNs to enhance online learning experiences. From delivering course content seamlessly to facilitating live virtual classes, CDNs play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and reliable educational experience for students and educators alike.
Gaming
The gaming industry requires a significant number of resources. This issue is the biggest challenge in this industry: delivering the best content while addressing lag issues. CDN technology helps online games create a "buffer zone" - where developers can store their entire game on CDN servers. In this situation, direct requests to the original server will no longer be necessary or will be minimized.
Logistics
In the logistics sector, where timely information is critical, CDNs play a pivotal role in ensuring swift and efficient communication. From tracking shipments to managing inventory, CDNs help logistics companies deliver real-time data, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
E-commerce
Ecommerce platforms heavily rely on CDNs to provide a seamless shopping experience. While the products may vary, users have limited time. If a website cannot deliver sufficient essential information within 1 second, the opportunity to reach customers will be lost. Ecommerce requires a CDN to manage requests from diverse locations. By storing content in the nearest location to the user, a CDN can effectively mitigate sudden surges in server traffic.
Retail
In the retail industry, CDNs are instrumental in optimizing online storefronts. They contribute to faster loading of product images, efficient order processing, and a smoother overall shopping journey. Retailers use CDNs to provide a reliable and engaging online shopping experience for customers, ultimately driving sales and customer loyalty.
Professional Services
Professional service providers, such as consulting firms and legal services, utilize CDNs to deliver content securely and efficiently. Whether sharing documents, conducting virtual meetings, or accessing resources remotely, CDNs ensure that professionals can collaborate seamlessly and access information without delays.
vCDN solution from VNG Cloud
vCDN is a content delivery network developed by VNG Cloud. With servers strategically positioned in multiple locations, equipped with extremely high bandwidth, vCDN significantly boosts website and mobile application speed. This results in an enhanced user experience and increased customer satisfaction.
Remarkable products of vCDN: VOD, Live Streaming, Web Accelerator, và Object Download.
With vCDN services, businesses can:
- Protecting the website from DDoS attacks: vCDN utilizes a distributed architecture to shield the website from DDoS attacks and minimize the damage caused by such attacks.
- Improving Google Ranking and SEO: vCDN enhances Google Ranking and SEO by optimizing access speed and improving website performance.
- Bandwidth and cost optimization: vCDN reduces the load on the origin server and optimizes bandwidth usage, resulting in cost savings.
- Increasing concurrent user access: vCDN supports serving many users simultaneously across various locations, enhancing the capacity and user experience.
- High readiness & easy to deploy: vCDN ensures high readiness and reliability, keeping the website running smoothly and consistently. Moreover, it is easy to integrate and deploy vCDN quickly.
To check out the latest vCDN promotion, please click here. For technical assistance, contact VNG Cloud now at Hotline 19001549 – Ext 1.